KEY FEATURES
COMMUNITY/ GEOGRAPHY
Community leaders
Health education programs focused on adult women
United States
COMMUNITY ENGAGEMENT OUTCOMES
Strengthened partnerships + alliances
Diversity + inclusivity
Shared power
Structural supports for community engagement
Improved health + health care programs + policies
Community-aligned solutions
PLACE(S) OF INSTRUMENT USE
Community/community-based organization
LANGUAGE TRANSLATIONS
Not specified
PSYCHOMETRIC PROPERTIES
Construct validity
Content validity
Internal consistency reliability
YEAR OF USE
1991-1992
Assessment Instrument Overview
The Community Ownership Scale has 14 questions and is used by community leaders. It monitors efforts that foster community ownership, defined as the amount of control community leaders have within a program. It also assesses the relationships between perceived ownership and program effectiveness and maintenance over time.
Alignment with Assessing Meaningful Community Engagement Conceptual Model
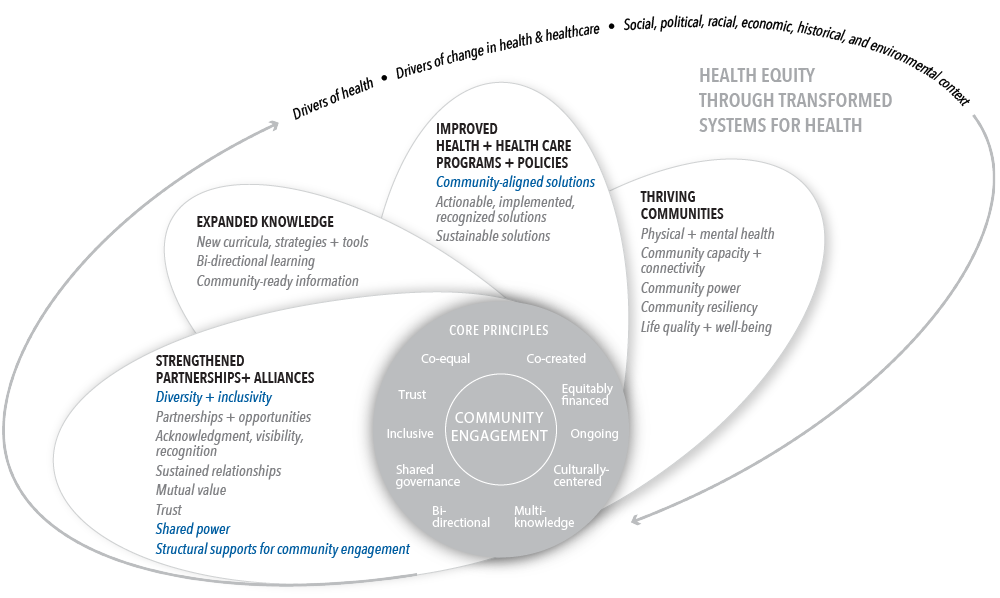
The questions in the Community Ownership Scale were realigned to the Assessing Community Engagement Conceptual Model. Figure 1 displays the alignment of the Community Ownership Scale with the Conceptual Model domain(s) and indicator(s). Where an instrument is mapped broadly with a domain or with a specific indicator, the figure shows the alignment in blue font.
Table 1 displays the alignment of the Community Ownership Scale’s individual questions and validated focus areas with the Conceptual Model domain(s) and indicator(s). The table shows, from left to right, the aligned Conceptual Model domain(s) and indicator(s), the individual questions from the Community Ownership Scale transcribed as they appear in the instrument (with minor formatting changes for clarity), and the validated focus area(s) presented in the article.
| CONCEPTUAL MODEL DOMAIN(S) AND INDICATOR(S) | ASSESSMENT INSTRUMENT QUESTIONS | VALIDATED FOCUS AREA(S) |
| STRENGTHENED PARTNERSHIPS + ALLIANCES; Diversity + inclusivity | (12) How much influence would you say that the (university staff/local program staff/community leadership) has on hiring and evaluating the professional staff of the [insert program name] program?* | Ownership |
| STRENGTHENED PARTNERSHIPS + ALLIANCES; Shared power | How much influence would you say that the (university staff/local program staff/community leadership) has on
| |
| STRENGTHENED PARTNERSHIPS + ALLIANCES; Structural supports for community engagement | How much influence would you say that the (university staff/local program staff/community leadership) has on
| |
| IMPROVED HEALTH + HEALTH CARE PROGRAMS + POLICIES; Community-aligned solutions | How much influence would you say that the (university staff/local program staff/community leadership) has on
|
*Note that these questions are duplicated to reflect their alignment with multiple domains and/or indicators in the Conceptual Model.
Table 1 | Community Ownership Scale questions and alignment with the domain(s) and indicator(s) of the Assessing Community Engagement Conceptual Model
ASSESSMENT INSTRUMENT BACKGROUND
Context of instrument development/use
The article details the development and testing of the Community Ownership Scale to support partnerships between three community health education programs and a university research group. The community health education programs shared a common model for behavior change that predicted community leader reliance on the research group would decrease as the programs matured. Two programs supported county-wide efforts to reduce cigarette smoking among women and one county-wide program promoted breast cancer screening. The Community Ownership Scale was developed and tested in the early stages of the three programs. It identified key programmatic functions, at different stages in the program, for monitoring efforts to foster community ownership and assess the relationships between perceived ownership and program effectiveness and maintenance.
Instrument description/purpose
The Community Ownership scale emphasizes one validated (i.e., construct) focus area:
- Ownership
The Community Ownership Scale measures the amount of control the three parties involved in the programs – community leaders, the external sponsoring agency, and the local program staff – have in the areas of goal setting, planning, program design and implementation, personnel, and budget develop. The Community Ownership Scale consists of 14 questions with a four-point Likert response structure ranging from “none” to “a lot.”
For each function, community leaders provide ratings for each of the three parties. Scores are averaged for each function and for each of the three parties separately. A higher aggregate score for a party means that community leaders perceived that party as having a greater degree of program ownership.
The Community Ownership Scale can be accessed through the link here: https://nam.edu/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/Community-Ownership-Scale-Title-Page-and-Instrument-v2_TL.pdf.
Engagement involved in developing, implementing, or evaluating the assessment instrument
A preliminary list of key functions was developed using descriptions from the literature of similar health education programs, observations of the three programs, discussions with the university research staff members, and semi-structured interviews with three community leaders from the programs. A draft instrument was then developed and reviewed by a community organization specialist from another institution, six university research staff members with community organization experience, five local staff members from the three programs, and the community leaders interviewed previously to develop the key functions. Based on the reviews, the language in the instrument was revised or tailored to individual programs and several items were added to the instrument. Program leaders from the community health education programs were a part of the development process and tested the instrument.
Additional information on populations engaged in instrument use
Not specified.
Notes
- Potential limitations: The Community Ownership Scale was designed for programs where community leaders, an external agency, and local staff interact. The three programs included in the study were very similar (i.e., focused on health behavior issues for adult women, used comparable community organization models, and were initiated by the same university group). These factors, as well as the structure and content of the instrument, limit the generalizability of the results.
- Important findings: The study results indicated that leaders from two of the three programs (Program A and B) believed they had more influence compared to the external agency for 10 out of 14 of the same program functions. For the three other program functions, they felt they had less influence than the external agency. Leaders from Program C did not identify any program functions where they felt they had more influence than the external agency.
- Future research needed: Based on the results presented in this article, the Community Ownership Scale has shown preliminary evidence of validity. Additional steps to assess validity should be taken, such as administering the instrument in later stages of the programs and testing variations of the instrument in other programs.
- Supplemental information: Additional research has been conducted using the Community Ownership Scale on other populations (i.e., programs focused on low-income older adults). Information on this research and further modifications made to the instrument can be found in the following article:
- Armbruster, C., B. Gale, J. Brady, and N. Thompson. 1999. Perceived Ownership in a Community Coalition. Public Health Nursing 16(1):17–22. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1525-1446.1999.00017.x.
We want to hear from you!
Assessing community engagement involves the participation of many stakeholders. Click here to share feedback on these resources, or email [email protected] and include “measure engagement” in the subject line to learn more about the NAM’s Assessing Community Engagement project.
Related Products